Have you ever wondered about how and why there is so much spam everywhere? The origins of modern spam can be traced back to the early days of email. The term “spam” in this context is believed to have originated from a Monty Python sketch in which the word “spam” is repeated excessively. However, spam can be traced back to 1864 when the first unsolicited electronic messages were believed to have been transmitted via telegraph. The messages themselves contained suspicious investment opportunities.
In the early 1990s, what we know today as email spam, began to proliferate, typically consisting of unsolicited commercial messages and advertisements. Early spam messages were often simple and straightforward, offering products or services.
Historically, spam has taken various forms over the years, dating back to well before the internet, but the term “spam” is most commonly associated with unsolicited and often annoying or harmful messages distributed via electronic communication channels. The history of spam is closely tied to the development of electronic communication technologies, particularly email, and it reflects the evolving nature of advertising, promotion, and unwanted communication.

Here’s a brief overview of the historical evolution of spam:
- Pre-Internet Era: The concept of unsolicited communication predates the internet. Chain letters and pyramid schemes were early forms of postal mail spam. These letters were sent via traditional mail and asked recipients to send money or items to the person at the top of the chain, promising wealth in return.
- Emergence of Electronic Communication: The transition from traditional mail to electronic communication was a critical turning point. As the internet began to gain popularity, electronic messages became a new medium for unsolicited advertising.
- Bulletin Board Systems (BBS): Bulletin Board Systems (BBS) were a precursor to modern online forums and social media. Spammers would post advertisements and promotional messages on these BBS, targeting specific communities of users.
- Usenet Newsgroup Spam: Usenet newsgroups, which allowed users to engage in discussions on various topics, became a popular target for spammers. They would post messages promoting everything from get-rich-quick schemes to adult content.
- Anti-Spam Measures: As spam became more prevalent in Usenet newsgroups, users and system administrators developed tools to filter out unwanted content. This led to the creation of “killfiles” and other filtering methods to reduce spam’s impact.
- The Rise of Email: As email usage grew, so did email spam. Spammers sent bulk email messages to large lists of addresses, which often contained unsolicited commercial content. Some spammers used tactics like “email bombing,” where they would flood a recipient’s inbox with a large volume of spam messages, overwhelming their email client.
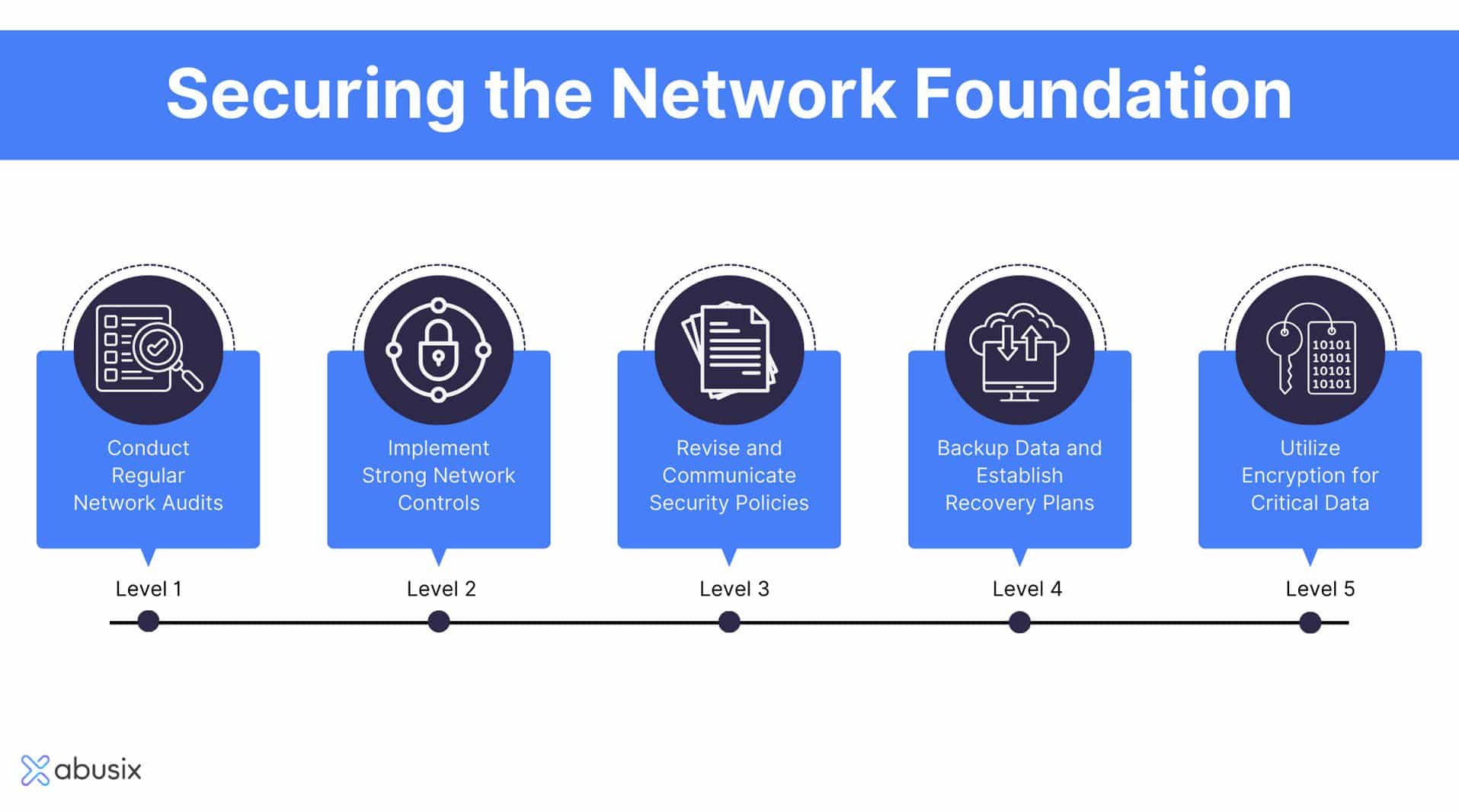
- Legal and Technological Responses: Governments and technology companies began to take action against spam. Laws such as the CAN-SPAM Act in the United States and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) set guidelines for legitimate email marketing.
Email providers developed spam filters and implemented rules to detect and block spam. - Evolving Tactics: Spammers adapted to anti-spam measures by using more sophisticated techniques. This included using images instead of text to evade text-based filters and sending phishing emails aimed at stealing personal information.
- Expansion to Other Communication Platforms: With the rise of social media, instant messaging, mobile phones, and various other communication channels, spammers expanded their activities to target these platforms. This included sending spam via text messages, creating fake social media profiles, and posting spam in comments and reviews. This will be covered in Part 2 of this blog series.
- Malicious Intent: Spam has also evolved to become more malicious, with the distribution of malware, ransomware, and phishing attacks. These attacks aim to compromise personal information, computers, and even entire networks.
Throughout its history, spam has continually adapted to exploit emerging communication technologies and platforms. It remains a persistent challenge for users, businesses, and organizations, necessitating the development of advanced spam filters, security measures, and legal regulations to combat this ever-evolving problem.