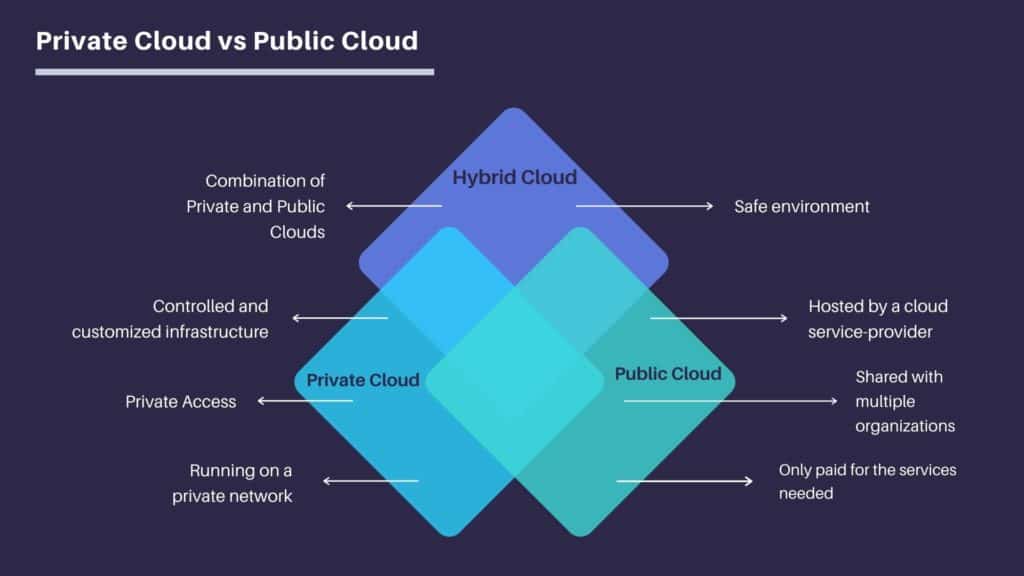
There’s no doubt that cloud migration is all the rage, but organizations have multiple choices when it comes to migrating their storage and systems. A private cloud is accessible for a selected group of users who’ve subscribed to these services, and the general public can’t use it.
On the other hand, the public cloud is accessible to all. Most internet users now utilize some form of the public cloud to store personal files, and the number is predicted to grow significantly.
There are pros and cons to both public and private clouds, but one issue is especially critical for business: security. Let’s take a look at the two cloud types and how you can enforce cloud security in your organization.
The importance of cloud security
Cloud security consists of different policies, procedures, technologies, and controls that collaborate to protect the cloud system infrastructure.
Cloud security rules are enforced by the provider to protect the clients’ privacy, data, and crucial information. They also authenticate access and filter traffic. The particular security measures depend on the cloud provider and type of cloud an organization is using.
With either type, the attack surface is widened with cloud use, and this makes it imperative to keep your cloud security system up-to-date. This is the only way to ensure that it has the ability to fight external and internal threats and keep cloud data safe and secure.
Cloud security is particularly important if you are storing sensitive business data in your cloud servers. For example, if you use cloud-based accounting software, you should look for tools that come with crucial features like PCI-DSS certification. Let’s explore how this challenge differs in public vs. private cloud setups.
What is Private cloud?
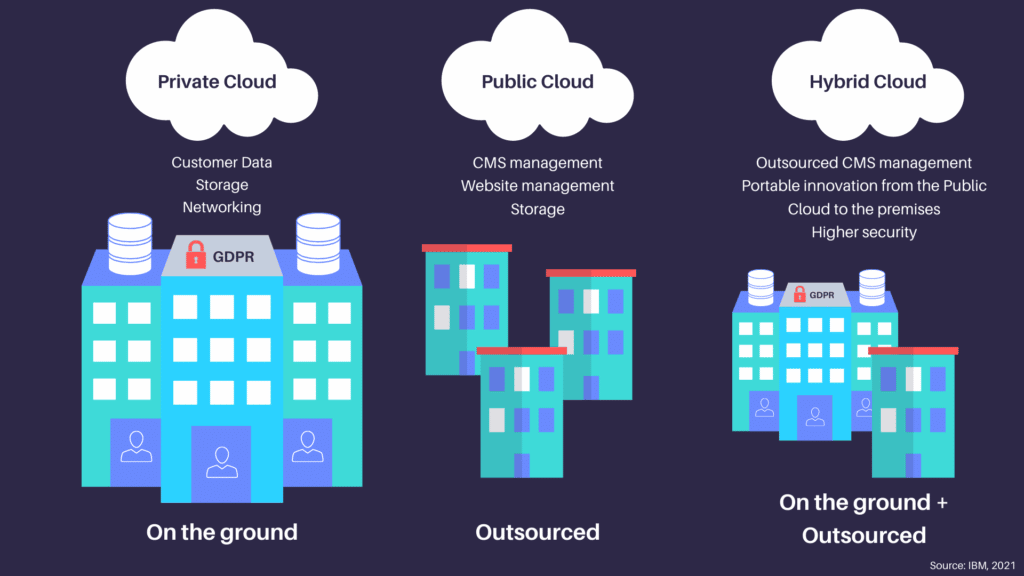
A private cloud is a cloud computing system used by selected users only. It has all the hardware and software resources of a public cloud, but not everyone can access it. Private clouds often require the same management and maintenance responsibilities as a traditional data center.
Private clouds are primarily situated in the customer’s data center, providing remote single-tenant access. However, some private clouds are hosted by independent cloud providers. In those cases, customers can choose to have partial or complete management rights, and it is important to read the service license agreements to understand what security responsibilities the host is taking upon itself.
Many companies make private cloud their first choice because it is easier to meet its regulatory compliance requirements. This is viewed as more confidential for sensitive data, making it the primary choice of most organizations. But security can still be a concern, even without public access systems, so organizations should think about the pros and cons before choosing a type:
Positives:
- Exclusive access to cloud servers
- Customized infrastructure (including for security)
- Companies are instantly alerted about anyone with cloud access
- No risk of lost data or downtime if a central cloud server shuts down
Drawbacks:
- Companies need to regulate their protections, as it is solely their responsibility
- More expensive to obtain and maintain
- Less scalable than public clouds and require more IT power
What is a Public cloud?
A public cloud is always managed by third-party providers. Unlike the private cloud, it is shared between multiple organizations and individual users. Public cloud service providers offer three main types of cloud-based services, Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), Platform as a service (PaaS), and Software as a service (SaaS). Organizations can use these services either on a fixed monthly fee or a pay-per-use basis.
Public cloud providers use multiple data centers that are virtually partitioned to allow multiple users. Users have to pay extra costs for renting those partitioned places and additional services such as software applications, app development tools, or storage.
Most companies use the public cloud to store less sensitive data that does not require frequent access. The convenience of the public cloud is often viewed as a tradeoff with security.
Positives:
- Less expensive to use and maintain
- Highly scalable and useful for maximizing computing and storage
- Providers offer quick and straightforward disaster recovery services
- Businesses can add or subtract resources depending on their needs
Drawbacks:
- Security is in the provider’s hands
- Pay-per-use can be expensive in the long term
- Companies cannot personally design their system in a public cloud
Which cloud is more secure?
Even though companies prefer to use the private cloud over the public cloud to store sensitive information, it begs the question, is the private cloud really more secure than the public cloud? The answer is not so simple.
It is a big misconception that a private cloud has an innately better security system. For example, companies can easily download malware or viruses from other electronic devices connected to a private system. If companies want to secure their networks entirely, they must keep a separate internet portal for the cloud.
A competent hacker will use a number of methods to steal data or install malware software. However, there is invisibility in numbers. A hacker must know the exact cloud location to have access to it. In a public cloud, it is tough to determine the exact virtual location of a particular user’s data. So, the vast number of partitioned clouds acts as a sort of invisibility cloak to save companies from external threats.
Alternatively, the option of a Hybrid Cloud can help to solve your problems. A hybrid cloud can help you scale when needed, improve security for sensitive data and easily adapt to new technologies.
The hybrid cloud started out in 2011 as an alternative to the traditional ones: public and private clouds. Essentially, if you are using a private cloud, this model allows you to migrate the necessary services to the public cloud (whether it be Saas, Paas or Iaas) when you need it, while still maintaining some applications in your private cloud (IBM, 2021).
Which cloud is better for business?
A suitable cloud computing system for your business depends on the goals of a company.
The public cloud is likely better for new startups and smaller companies that lack financial resources to build their own systems. It is perfect for them to start from the public cloud to maintain their infrastructure efficiently and cost-effectively while meeting minimum requirements.
In contrast, the private cloud is most suitable for businesses with vast and unpredictable computing needs that require direct control and high security. Similarly, if your system gets a lot of traffic spikes, you might end up paying a lot with pay-per-use public access. Companies that can handle the maintenance and costs should go for private clouds if they want a more custom, secure option.
Finally, considering the hybrid cloud can be a great strategy. This option gives you the ability to move workloads as you need, scale your business and resources up and down, have access to instant innovation without the need to allocate resources, and have higher security.
What’s your pick?
Choosing a private cloud vs. a public cloud solution (or even a hybrid cloud) depends on a number of factors, but you must ensure that security is one of the chief considerations. Before undertaking your cloud migration, be sure to consult a security expert who can help you determine which cloud is best for your organization’s use and security needs.




